Central banks are increasingly exploring the integration of blockchain technology into traditional finance (TradFi), with smart contracts emerging as a potential tool for implementing monetary policy in tokenized environments. A recent joint research study, dubbed Project Pine, conducted by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Innovation Center and the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) Innovation Hub Swiss Centre, highlights the potential of smart contracts in providing central banks with flexible and rapid-response capabilities within a tokenized financial system.
This initiative signals a growing interest in leveraging blockchain technology to modernize and streamline traditional financial operations. Project Pine specifically focused on testing a prototype of a “generic customizable monetary policy tokenized toolkit” intended for further research by central banks, according to a BIS report published on May 15.
The BIS report emphasized the speed and flexibility offered by the smart contract toolkit, stating, “The smart contract toolkit was fast and flexible. In hypothetical scenarios, the central bank was able to add and change tools instantly.” This suggests that smart contracts could enable central banks to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and implement policy adjustments in real-time.
The report further underscores the potential significance of smart contracts in the execution of monetary policy if tokenization becomes widely adopted for money and securities.
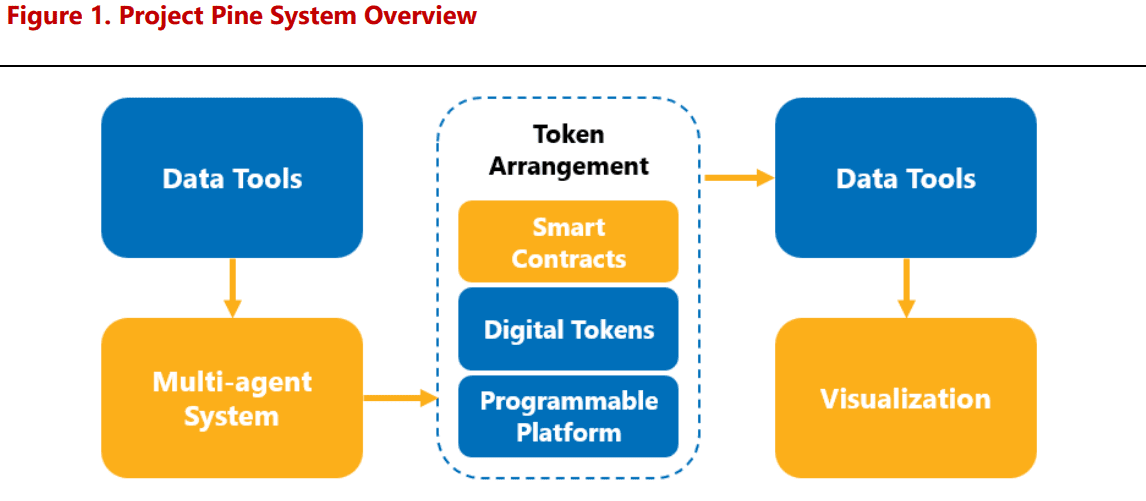
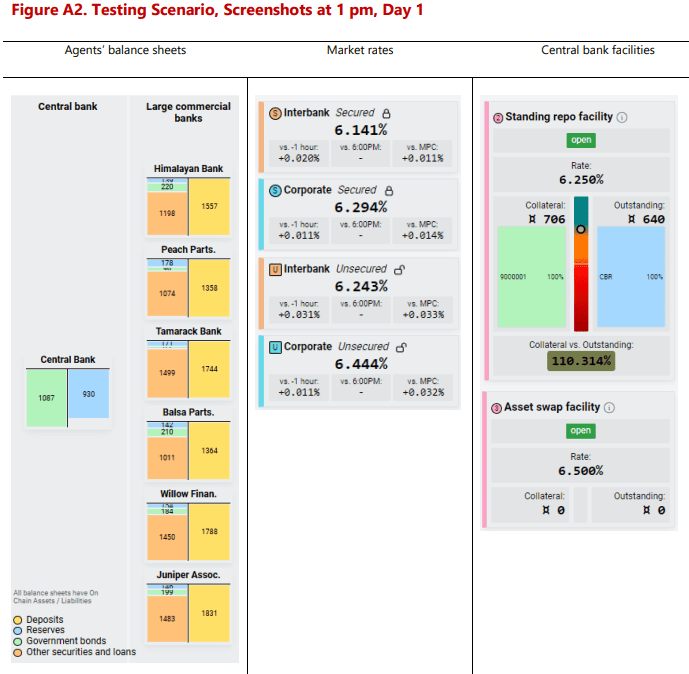
Project Pine represents a “first step” in demonstrating the potential benefits of tokenization for central banks, according to the BIS. The framework’s speed and consistency were validated within a 10-minute hypothetical scenario where central banks swiftly adjusted collateral criteria and exchanged liquid collateral for illiquid assets amid declining collateral values.
Moreover, the smart-contract framework facilitated the deployment of a new facility offering reserves and the immediate modification of interest rates on those reserves.
How Smart Contracts and Tokenization Can Aid Central Banks
The BIS report suggests that smart contracts and tokenization technology could significantly enhance central banks’ ability to respond rapidly to “extraordinary events.”
Key benefits highlighted include:
- Speed and Efficiency: Smart contracts automate processes, enabling quicker implementation of monetary policy decisions.
- Flexibility: Central banks can adjust parameters and deploy new facilities in real-time, adapting to unforeseen circumstances.
- Transparency: Blockchain technology provides a transparent and auditable record of transactions.
The report states:
“This speed, coupled with the ability to adjust any of the parameters at any time, gives central banks flexibility in responding to unforeseen events and fast-moving crises.”
However, the report also acknowledges potential challenges. A significant hurdle is the infrastructure limitations within existing central banking systems, which are not designed for these advanced use cases. Adapting current systems or building new infrastructure will be crucial for successful implementation.
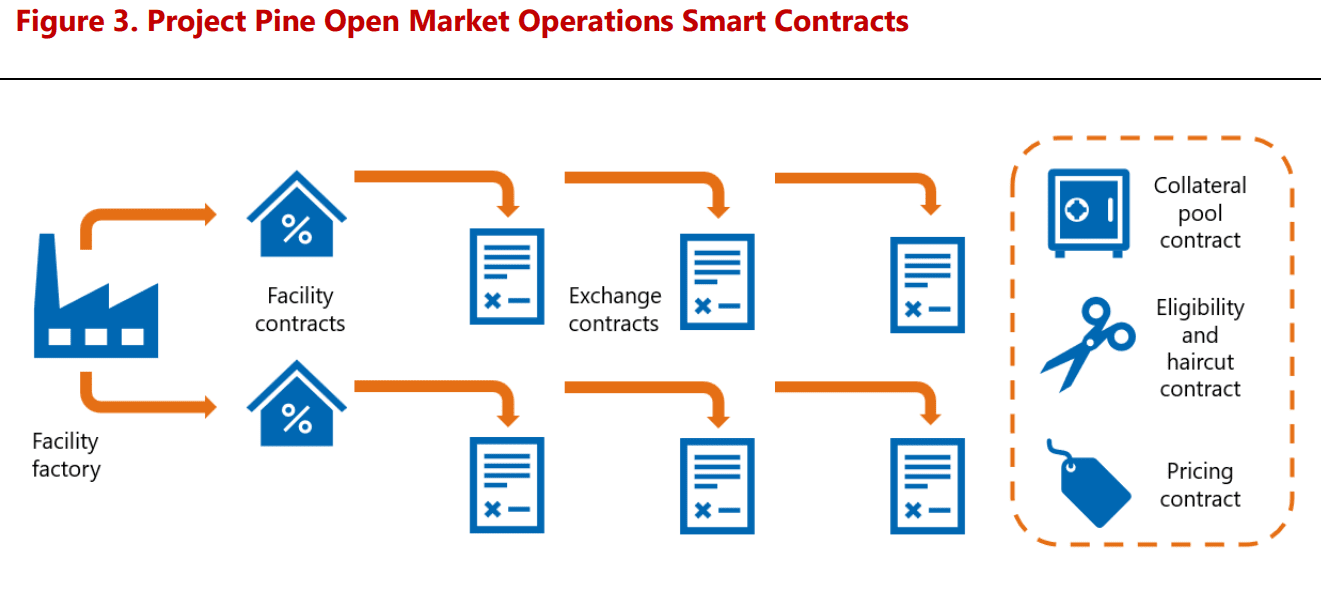
Project Pine utilized Ethereum’s ERC-20 token standard combined with another standard for access control, demonstrating the potential for interoperability and standardization within the tokenized financial system.
The increasing embrace of tokenization by financial institutions underscores its potential. At the Consensus 2025 conference, Joseph Spiro, product director at DTCC Digital Assets, described stablecoins as the “perfect” financial instrument for real-time collateral management for financial transactions such as loans or derivatives, highlighting another area where tokenization could significantly improve efficiency.
The Future of Central Banking and Blockchain
Project Pine and similar initiatives demonstrate a growing recognition within central banking circles of the potential benefits of blockchain technology. While challenges related to infrastructure and regulatory frameworks remain, the exploration of smart contracts and tokenization represents a significant step toward modernizing monetary policy implementation.
Potential Implications and Further Considerations:
- Regulatory Clarity: Clear regulatory frameworks are needed to govern the use of smart contracts and tokenized assets in the financial system.
- Cybersecurity: Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect against potential attacks on blockchain-based systems.
- Interoperability: Ensuring interoperability between different blockchain networks and traditional financial systems is crucial for widespread adoption.
- Scalability: Blockchain networks need to be scalable to handle the high transaction volumes of the financial system.
As central banks continue to explore the potential of blockchain technology, further research and development will be necessary to overcome these challenges and unlock the full potential of smart contracts and tokenization for monetary policy implementation.