Group of Seven (G7) leaders are expected to address North Korea’s growing cyber threats and cryptocurrency heists at their upcoming summit in Canada. While conflicts in Ukraine and Gaza are primary concerns, North Korea’s illicit cyber operations have become a critical issue demanding a unified international strategy.
North Korea’s cyber activities, particularly crypto theft, have become a significant funding source for the regime’s programs. Hacking groups, notably the Lazarus Group, have stolen billions in cryptocurrency, with one major incident being the $1.4 billion hack on Bybit in February, marking the largest ever in the crypto industry.
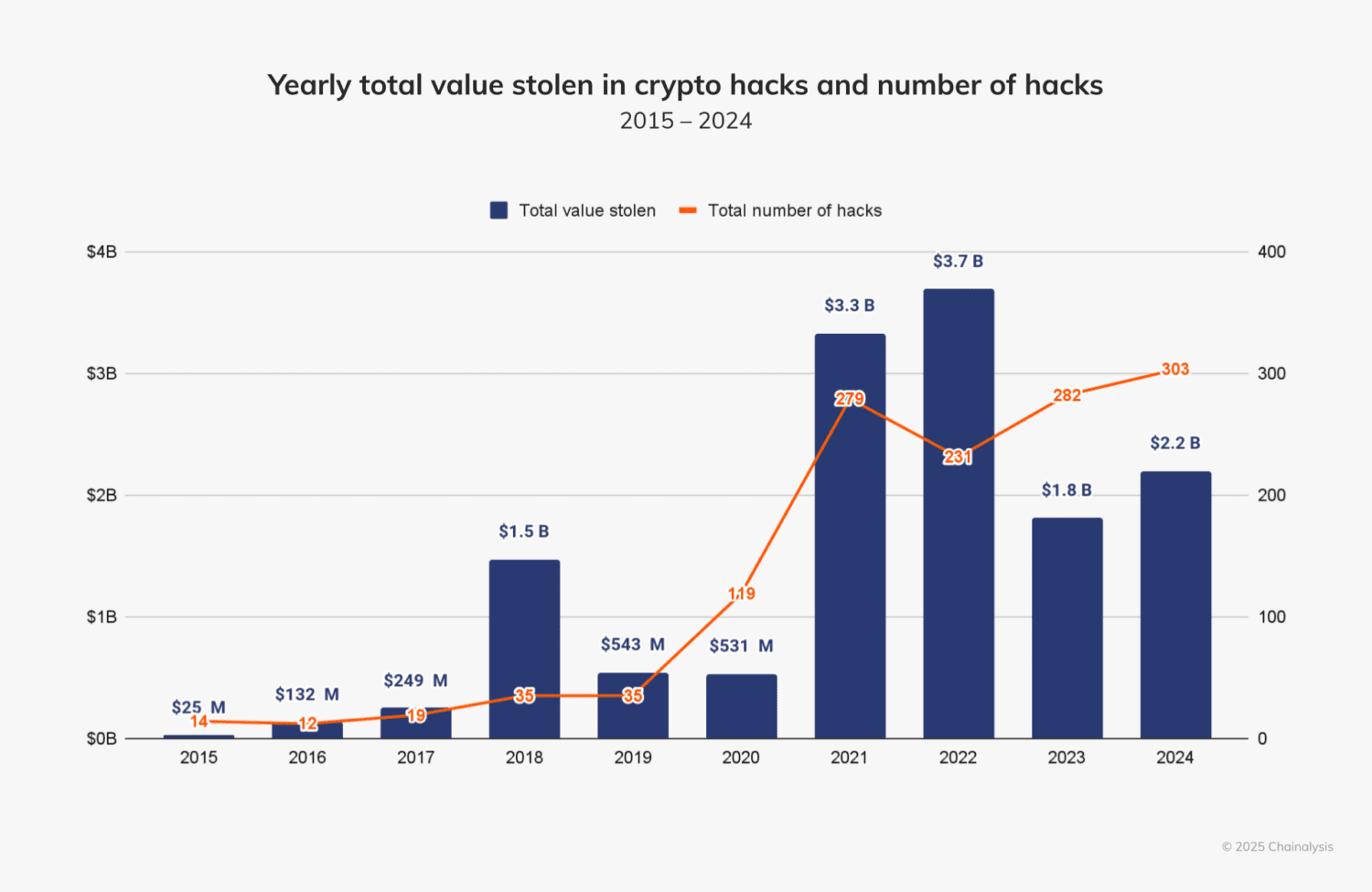
Chainalysis reports that North Korean hackers stole over $1.3 billion through 47 crypto heists in 2024 alone. A joint warning issued by the US, Japan, and South Korea highlighted North Korea’s deployment of tech workers to infiltrate crypto companies as insider threats.
A US Treasury report indicated that the illicit proceeds from these hacks enable North Korea to bypass international sanctions and fund its weapons development programs.
North Korea’s Evolving Cyber Tactics
North Korea’s cyber operations have evolved, demonstrating increased sophistication. These tactics include:
- Direct Crypto Theft: Stealing cryptocurrency from exchanges and individuals.
- Insider Threats: Infiltrating crypto companies with tech workers.
- Shell Companies: Setting up shell companies to deliver malware and scam crypto developers.
- Freelance Work: Securing freelance jobs online to gain access to crypto projects.
Examples of North Korean Cyber Activities
Several incidents highlight North Korea’s cyber capabilities:
- Bybit Hack: The Lazarus Group’s $1.4 billion theft from Bybit.
- Kraken Infiltration Attempt: A foiled attempt by a North Korean hacker to infiltrate the Kraken exchange.
- Shell Companies: Lazarus Group establishing shell companies in the US to distribute malware.
- Fake Job Interviews: North Korean operatives using fake job interviews to gather information and potentially infiltrate organizations.
Implications and International Response
North Korea’s cyber activities have significant implications:
- Funding Weapons Programs: Crypto theft provides a crucial funding source for North Korea’s weapons development.
- Circumventing Sanctions: Illicit proceeds allow North Korea to bypass international sanctions.
- Threat to Crypto Industry: Cyberattacks undermine the security and stability of the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
The G7’s discussion of North Korea’s cyber threats signals a commitment to a coordinated international response. Potential measures include:
- Increased Sanctions: Imposing stricter sanctions on entities involved in North Korea’s cyber activities.
- Cybersecurity Cooperation: Enhancing collaboration among nations to share threat intelligence and develop defensive strategies.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Establishing stronger regulatory frameworks for the cryptocurrency industry to prevent money laundering and illicit financing.
- Public Awareness: Raising awareness among crypto users and companies about the risks posed by North Korean hackers.
Conclusion
The G7 summit’s focus on North Korea’s crypto hacking underscores the urgent need for a comprehensive international strategy to counter these threats. By addressing the financial lifeline that cryptocurrency provides to the regime, the international community aims to curb North Korea’s illicit activities and promote global security.