Key Takeaways
- Stop-Loss Orders: Limit potential losses by automatically selling Bitcoin when the price drops to a predetermined level.
- Take-Profit Orders: Secure profits by automatically selling Bitcoin when the price reaches a desired target.
- Risk Management: These orders help manage risk in Bitcoin’s volatile market and remove emotional decision-making.
- Strategic Importance: Proper setup requires understanding market volatility, support levels, and avoiding common pitfalls.
Bitcoin trading, known for its volatility, presents both opportunities and risks. Stop-loss and take-profit orders are essential tools for managing these risks and securing profits. These automated orders allow traders to define specific price points at which to either cut losses or realize gains, ensuring a disciplined approach to trading.
What are Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders?
Stop-loss and take-profit orders are instructions set on a trading platform to automatically close a position when the price reaches a certain level. They serve distinct purposes:
- Stop-Loss Order: An order to sell an asset when it drops to a specified price, limiting potential losses.
- Take-Profit Order: An order to sell an asset when it rises to a specified price, securing profits.
These orders are particularly useful in volatile markets like Bitcoin, where prices can fluctuate rapidly and unexpectedly. They help traders avoid emotional decision-making and ensure trades are executed according to a predefined strategy.
Bitcoin Stop-Loss Orders: Limiting Losses
A stop-loss order is designed to protect capital by automatically selling Bitcoin if the price falls below a certain level. This is especially crucial in a market as volatile as Bitcoin, where sudden price drops can lead to significant losses.
Example: If you buy Bitcoin at $90,000 and set a stop-loss at $85,000, the order will automatically sell your Bitcoin if the price drops to $85,000, limiting your loss to $5,000.
Bitcoin Take-Profit Orders: Securing Gains
A take-profit order is used to lock in profits by automatically selling Bitcoin when the price reaches a predetermined target. This helps traders capitalize on gains and avoid the temptation of holding onto a position for too long, potentially missing out on profits due to market reversals.
Example: If you buy Bitcoin at $90,000 and set a take-profit at $95,000, the order will automatically sell your Bitcoin when the price reaches $95,000, securing a $5,000 profit.
Importance of Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
The importance of these orders in Bitcoin trading cannot be overstated. They provide several key benefits:
- Risk Management: They help manage the inherent risks of Bitcoin trading by limiting potential losses and securing profits.
- Emotional Control: They remove emotions from trading decisions, ensuring trades are executed based on a predetermined strategy.
- Automation: They automate the trading process, allowing traders to manage positions even when they cannot actively monitor the market.
Setting Up Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
The process of setting up these orders varies slightly depending on the trading platform, but the general steps are as follows:
- Choose a Trading Platform: Select a reputable platform like Binance, Coinbase Pro, or Kraken.
- Open a Trading Position: Navigate to the trading section, select the BTC pair (e.g., BTC/USD), and place a buy or sell order.
- Set Stop-Loss Price: Determine your risk tolerance and set the stop-loss price below your entry point for a buy order or above your entry point for a sell order.
- Set Take-Profit Price: Set the take-profit price above your entry point for a buy order or below your entry point for a sell order, based on your profit target.
- Confirm and Monitor: Double-check the details and confirm the order. Monitor the order status and adjust as needed.
Here’s an example of setting up a stop loss and take profit order on Kraken.
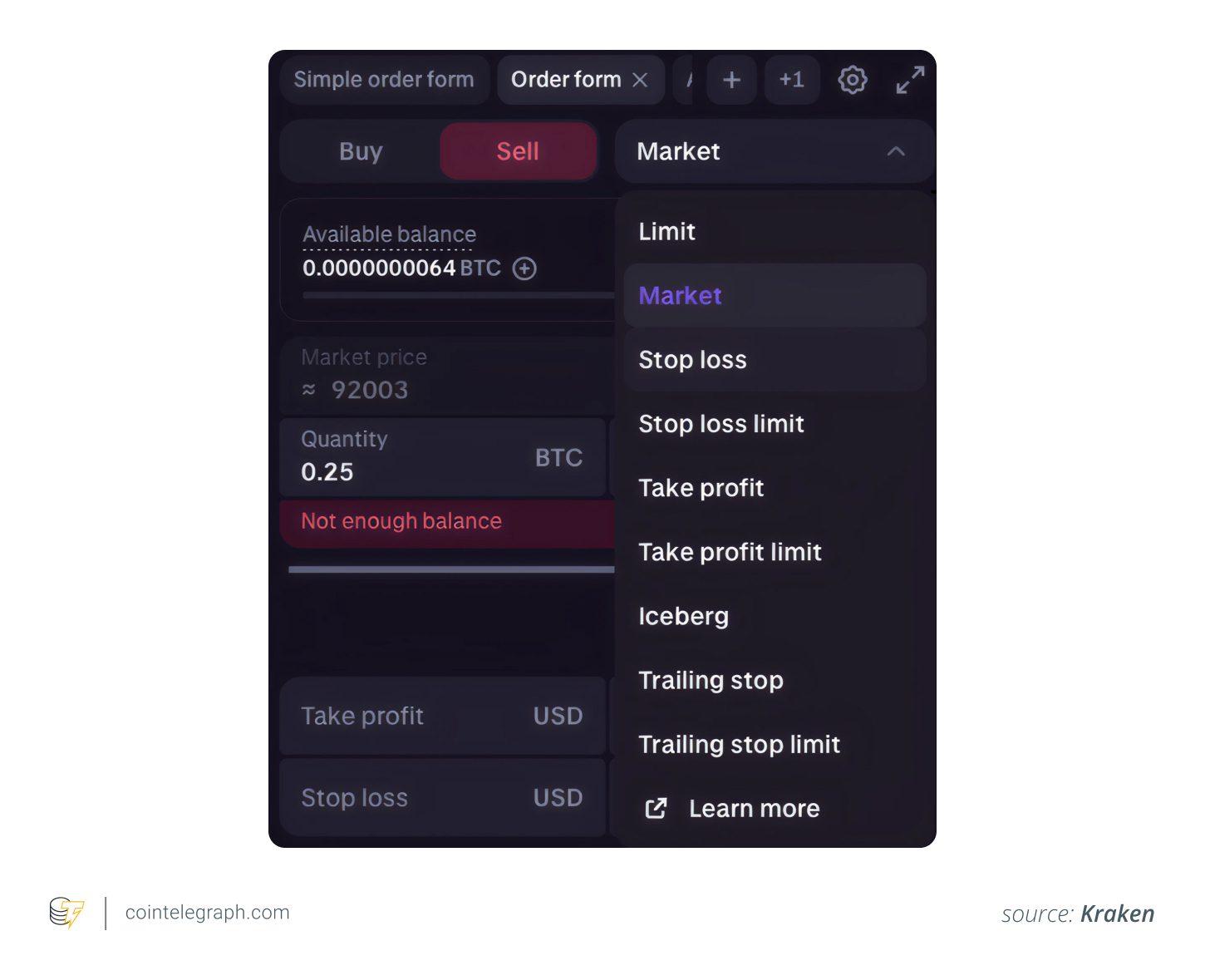
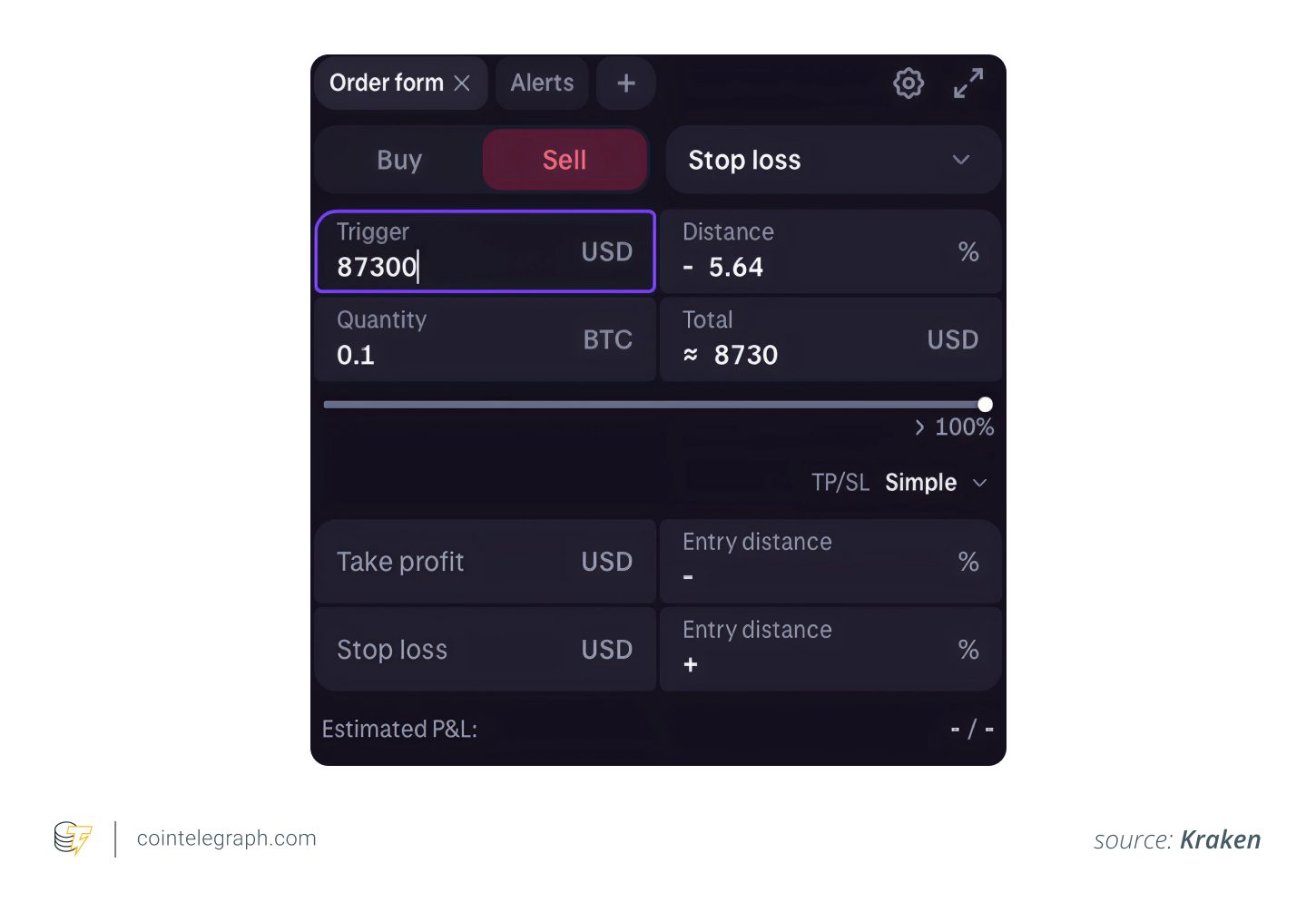
Best Practices for Stop-Loss Placement
Placing stop-loss orders effectively requires careful consideration of market dynamics. Here are some best practices:
- Consider Volatility: Use indicators like the Average True Range (ATR) to gauge volatility and set stop-loss levels accordingly.
- Align with Support Levels: Place stop-loss orders below key support levels to avoid premature triggering due to minor price fluctuations.
- Avoid Obvious Levels: Whales and bots often target stop-loss orders at round numbers. Place your orders slightly below or above these levels to avoid being targeted.
Trailing Stop-Loss Orders
A trailing stop-loss order automatically adjusts the stop-loss price as the market price moves in a profitable direction. This allows you to lock in profits while still protecting against potential losses. For example, set a trailing stop loss at 3%-5% below the peak price.
Account for Slippage
Slippage can occur during periods of high volatility or low liquidity, causing the actual execution price to differ from the expected price. To mitigate this, widen the stop-loss slightly by 0.5%-1%.
Adjusting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders
Adjusting these orders is crucial to adapt to changing market conditions.
When and How to Adjust a Stop-Loss
- Tighten After a Move in Your Favor: As the price rises, move the stop-loss higher to lock in profits.
- Trail During a Trend: Use a trailing stop-loss to capture more upside during a bull market.
- Widen During Consolidation: Avoid tight stop-losses in unsettled ranges.
- Adjust Before Major Events: Tighten or widen the stop-loss based on the expected volatility of events like Fed announcements.
When and How to Adjust a Take-Profit
- Extend During Strong Momentum: If the price is rising rapidly, push the take-profit higher to maximize gains.
- Take Partial Profits at Key Levels: Sell a portion of your position at resistance levels.
- Tighten Near Resistance: Reduce the take-profit target as the price approaches resistance.
- Reset After a Pullback: If you miss a take-profit, reset the order after the price retraces.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can undermine the effectiveness of stop-loss and take-profit orders:
- Setting Stops Too Tightly: Use volatility metrics and support levels to avoid premature triggering.
- Ignoring Slippage: Account for slippage, especially during high volatility.
- Chasing Round Numbers: Avoid setting orders at obvious levels.
- Forgetting to Adjust: Regularly monitor and adjust orders based on market conditions.
- Misjudging Market Context: Adapt orders to current trends and sentiments.
- Not Accounting for Fees: Factor fees into profit targets.
- Panic-Canceling Orders: Stick to your initial plan and avoid emotional decisions.
By avoiding these mistakes and implementing a disciplined approach, you can effectively use stop-loss and take-profit orders to manage risk and secure profits in Bitcoin trading.
Disclaimer: This article does not contain investment advice or recommendations. Every investment and trading move involves risk, and readers should conduct their own research when making a decision.